
Researchers Explain Potential Cause of Earth’s Green Airglow
A team of Russian researchers from HSE University, the Russian Space Research Institute, and the Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism (Russian Academy of Sciences) has described the development of modulational instability of electromagnetic waves in dusty ionospheric plasma, which is caused by a high intensity of electromagnetic emissions. The researchers considered inelastic collisions of ionospheric plasma particles and formulated new tasks and applications to be addressed at a later stage. The results are published in the Physics of Plasmas journal.

Education and Employment in ‘Hard’ Science Provide no Salary Advantages Compared to ‘Soft’ Science at Any Career Stage
HSE University economists question whether Russian STEM specialists are better paid than non-STEM specialists. They compare wages of professionals with STEM and no STEM majors, and those working in STEM and no STEM jobs and explore how the gap evolves over the life cycle. They find that there is no advantage of STEM major and STEM job over their no STEM alternative. They present their findings in a paper published in the Voprosy Ekonomiki journal.

HSE University Center for Language and Brain Becomes World Leader in Just 10 Years
How can a small Russian research group become a world-famous scientific centre in less than a decade? A special edition of the Frontiers in Psychologyjournal devoted to increasing public awareness of neuroscience features an article about the HSE University Center for Language and Brain, including the successes and challenges of its early years.

Researchers Discover How to Obtain ‘Ideal’ 3D Cell Cultures for Cancer Research
A group of scientists from Hungary, Russia and Finland have developed a system capable of selecting cancer cells of a specific shape and size—spheroids. SpheroidPicker, the first AI device of its kind, enables a more standardized approach to working with tumour samples. The results of the research have been published in the journal Scientific Reports. One of researchers who worked on the project is Nikita Moshkov, Junior Research Fellow of the Laboratory on AI for Computational Biology.

The 'Curse' Is Lifted: Schooling Does Increase Graduates’ Salaries
Although many studies point to highly negative trends in returns to education in Russia, the situation actually appears to be stable and without any signs of overinvestment in human capital. This is the conclusion of Rostislav Kapeliushnikov, Deputy Director of the HSE Centre for Labour Market Studies and Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The results of his research are presented in the article ‘Returns to Education in Russia: Nowhere Below?’ published in the 8th issue of the Voprosy Ekonomiky journal.

New Data Gained on Double Perovskite Oxides
The Journal of Alloys and Compounds has published an article coauthored by the Institute of Solid State Chemistry and Mechanochemistry (the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences), the Donostia International Physics Centre, and the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics on the characteristics of cubic double perovskite oxides. To date, experimental measurements of the minerals’ characteristics have not corresponded to the results of theoretical modelling. The work marks the first time that researchers have set themselves the task of explaining this disparity. The data obtained will allow researchers to improve low-temperature fuel cell technologies—one of the main alternatives to current sources of electricity.

Researchers Confirm Correlation Between Education Expenditure and GDP Growth
HSE University researchers have analyzed the economic performance of almost a hundred countries to understand whether government investment in education pays off. The economists explain what kind of recommendations may be offered to governments—and how they vary based on a country's level of development—in the Voprosy Statistiki journal

HSE Scholars Determine Tsar Boris Godunov’s Exact Date of Birth
HSE University researchers Feodor Uspenskij and Anna Litvina studied the notes of Georg Tectander, a diplomat of the Holy Roman Empire, and discovered the exact date of birth of Tsar Boris Godunov: August 2 (Julian calendar) or August 12 (Gregorian calendar). The scholars then verified and confirmed this date with other 17th-century sources. The results of the study are presented in a paper published in the Studi Slavistici journal (Florence, Italy), and in a follow-up paper to be published by the same journal at the end of the year.

Businesses Benefit from Board Members’ Diverse Experiences
HSE researchers have assessed the influence of board members’ work experience diversity on a company’s economic performance. Who makes a better board member—company veterans or outsiders? Their findings have been published in the Russian Management Journal.
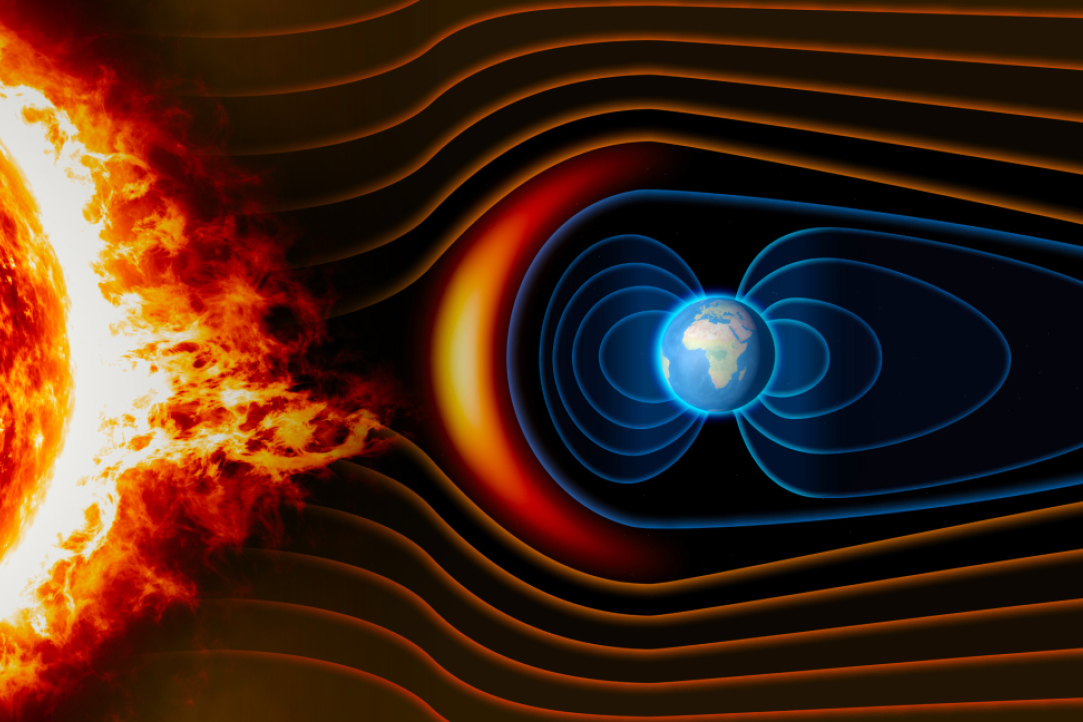
Russian Researchers Obtain New Data on Solar Magnetic Field Asymmetry
Researchers from the Institute of Earthquake Prediction Theory and Mathematical Geophysics (Russian Academy of Science) and HSE University have proven that asymmetry between meridional flows in the northern and southern hemispheres of the Sun depends on the anomalies of the solar magnetic field. Research undertaken by Elena Blanter and Mikhail Snirman reveals new aspects of the importance of solar magnetic field asymmetry for predicting the anomalies of the Sun’s activity. The article has been published in Solar Physics.
Deadline for applications to present academic reports - January 20, 2025