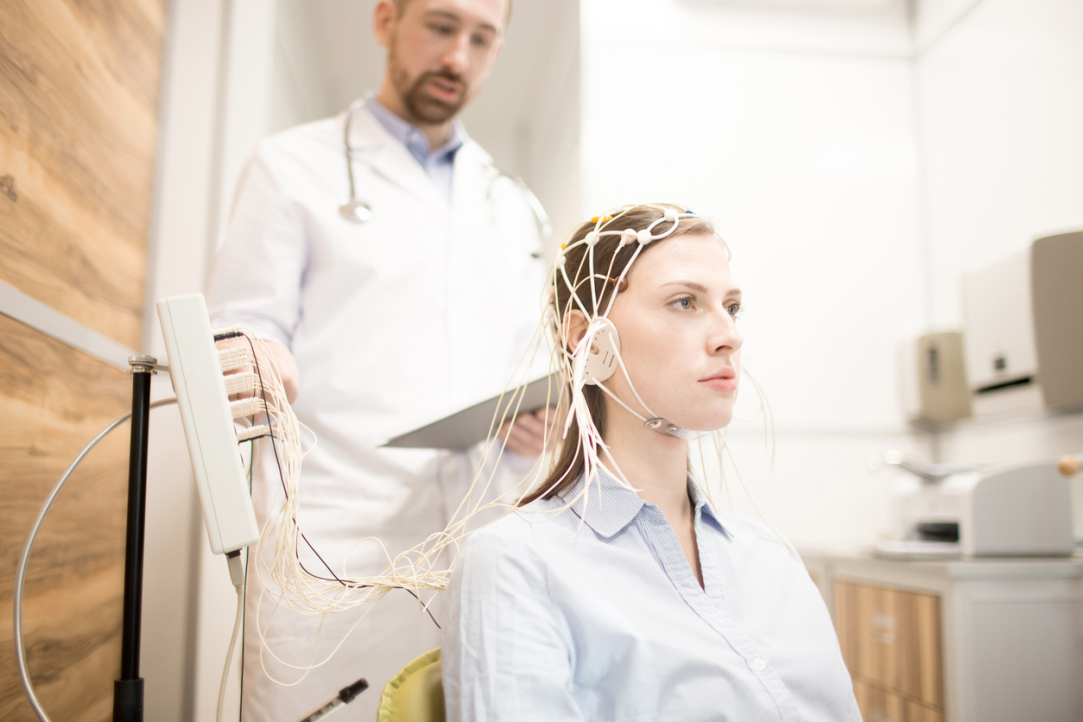
HSE Neuroscientists Use Neural Network to Enhance Neurofeedback Technology
Researchers from HSE University and the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (AIRI) have successfully lowered the latency between a change in brain activity and the presentation of the corresponding neurofeedback signal by a factor of 50. The results were obtained by employing a neural network trained in low-latency filtering of brain activity signals from diverse individuals. This approach opens up new prospects for the treatment of attention deficit disorder and epilepsy. A paper with the study findings has been published in Journal of Neural Engineering.

Financial Sector Risks Can Hinder Transition to Green Economy
According to HSE and MGIMO economists, increased financial sector risks in developed countries may be associated with a higher carbon footprint in banks' loan portfolios. This is likely due to the fact that in response to an unstable economic situation, banks tend to issue more loans to companies that have a detrimental impact on the environment. Although this might yield short-term profits for the banks, such trends hinder humanity's progress towards achieving a green economy. The paper has been published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
.jpg)
Online Rhythmic Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Can Reveal the Precise Moment When Preferences Shift in the Human Brain
Cognitive dissonance is a complex and multifaceted psychological phenomenon that arises in challenging decision-making scenarios. Multiple regions of the brain participate in its occurrence, yet the neurodynamics of underlying cognitive mechanisms remain a subject of debate. Researchers from the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have proposed the use of online transcranial magnetic stimulation applied to participants as they were actively engaged in tasks, to pinpoint the moment of cognitive dissonance resolution. Their findings have been published in a review paper in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.

A University's Special Status Is Correlated with a Substantial Increase in Salaries for Graduates
A university education is a highly sought-after commodity in Russia, yet the quality of universities and their programmes varies significantly. This gives rise to risks of inequality, both in the realm of education and in the labour market, and subsequently impacts the returns on higher education, which are manifested in the salaries earned by graduates. According to a study by Ilya Prakhov, Assistant Professor of the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, graduates from Russia’s top-tier universities enjoy a distinct advantage. The paper has been published in the International Journal of Educational Development.

Nanai and Chukchi Found Intolerant to 'Mushroom Sugar'
A team of researchers from HSE University, the RAS Research Centre for Medical Genetics, and the Moscow State University Institute of Anthropology have examined the impact of the human genotype on the production of trehalase, an enzyme responsible for metabolising 'mushroom sugar'. The researchers examined 1,068 DNA samples collected from inhabitants of northern and Arctic regions of Russia and found that the overall risk of trehalase deficiency in certain indigenous northern populations can be as high as 60–70%. The paper has been published in Problems of Nutrition.
.jpg)
News Finds You: HSE Researchers Study Media Consumption of People Who Avoid News
News avoidance is a global phenomenon that affects millions of people around the world. Despite their conscious refusal to consume media content, many argue that the most important news still finds them. Researchers at the HSE Laboratory for Studies in Economic Sociology have studied how people perceive the ‘news-finds-me’ effect. The results of the study were published in the Bulletin of Moscow University.

HSE Researchers Examine Wellbeing of Russian Social Media Users and Rank Public Holidays by Popularity
Researchers of the HSE Graduate School of Business trained a machine-learning (ML) model to infer users' subjective wellbeing from social media posts. Having processed 10 million tweets, the researchers compiled a rating of holidays celebrated in Russia based on their popularity. The New Year tops the list, but Russian-speaking users of Twitter are also happy to celebrate Defender of the Fatherland Day, International Women's Day, and Halloween. The study findings have been published in PeerJ Computer Science.

Good Deeds Bring Moral Satisfaction to Russians
Researchers from HSE University have analysed why people feel happier when they help others. It turns out that joy is caused by different reasons, depending on who we help — relatives or strangers. In both cases, happiness brings moral satisfaction from doing a good deed, but helping loved ones is also associated with satisfying the need for belonging and acceptance, while helping strangers provides a sense of autonomy. The results of the research were published in the Journal of Social and Personal Relationships.

Russian Radio Astronomers Discover a Method for Predicting Solar Flares
Researchers from HSE in Nizhny Novgorod and the Pulkovo Astronomical Observatory (CAO RAS) examined data on microwave emissions from several active solar regions. Astronomers discovered that a few hours prior to a flare, there was an increase in oscillations in the region with the highest observed brightness of the microwave emission during the flare. This method can potentially be used to achieve more accurate predictions of severe solar flares. The study has been published in Geomagnetism and Aeronomy.

Teaching Masters' Students and Conducting Lectures in English Boost Academic Productivity
HSE researchers have analysed teaching load data at the HSE campus in St Petersburg to investigate the potential impact of teaching on faculty research output. They found that factors such as teaching primarily masters' courses, conducting 20% of lectures in English, and supervising only one doctoral student per year were associated with a greater likelihood of producing more high-quality academic papers. The study has been published in Higher Education Quarterly.